The term Prehistory refers to the period before we began to write. Prehistoric events occur before the availability of written sources. There are no written records and decipherable documentation available for this period. Prehistory is understandable based on Artefacts, tools, pottery, and other physical things found on the various archaeological sites. Prehistoric culture is stone-age culture related to the history of human settlement. Let’s discuss in detail the stone-age culture.
Stone Age
The Stone age is a broad prehistoric period related to the evolution of human beings. This period started about 2.6 million years ago and lasted until the metallic age began.
Archaeologists have found some of the tools made of stone, bone, and wood, of which stone tools survived the best. Early humans used stone tools and weapons for hunting-gathering during this period. Most of these stone tools and other sources of the stone age were found during the archaeological excavations. Based on these archaeological shreds of evidence, we can divide the stone-age period into three parts.
- Palaeolithic Age (5,00,000 BCE to 10,000 BCE).
- Mesolithic Age (10,000 BCE to 6,000 BCE).
- Neolithic Age (6,000 BCE to 1,000 BCE).
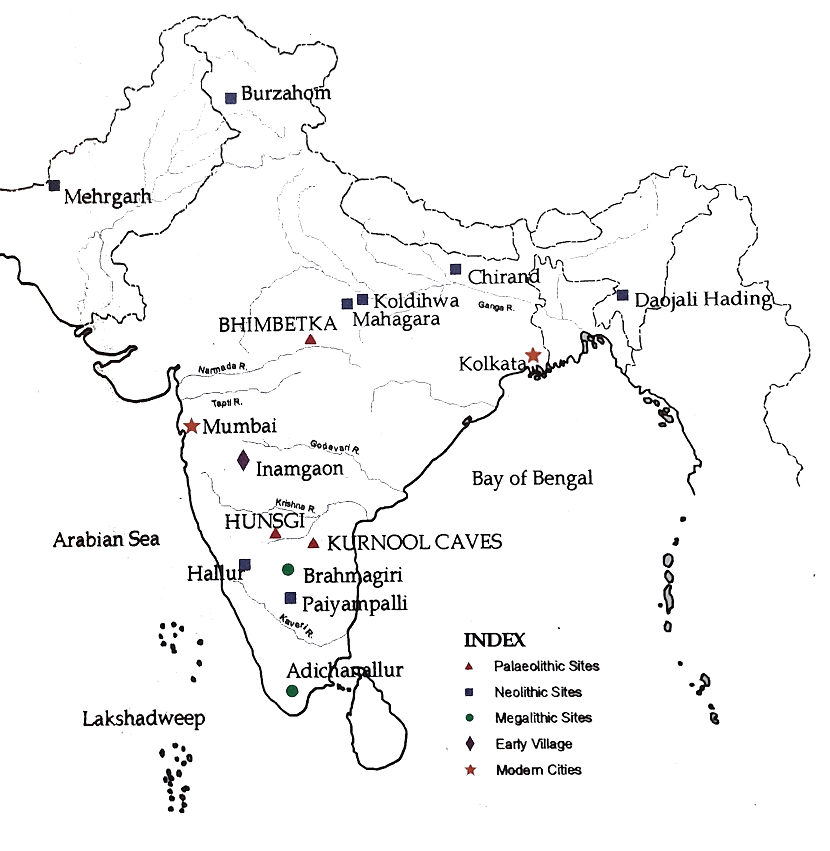
Palaeolithic Age (Old Stone age)
The term ‘Palaeolithic’ comes from two Greek words, ‘Palaeo‘ meaning old, and ‘lithos‘ meaning stone. This period was the earliest period of human evolution. The Palaeolithic age was part of the Pleistocene period (Ice Age) when the glaciers covered the earth with ice. The people of this age were described as hunter-gatherers. Archaeologists have found that early humans lived in caves and rock shelters. They ate gathered fruits & roots and also hunted wild animals.
Important characteristics of the Palaeolithic age
- The people of this age were dependent on hunting-gathering to fill their stomachs.
- They moved from one place to another for hunting. So, they had a nomadic lifestyle.
- They lived close to the rivers, caves, hilly areas, and rock shelters.
- They hunted the wild animals and gathered fruits, nuts, seeds, roots, and leaves for food.
- No agriculture was done during this period.
- People of this age do not know about pottery and house construction.
- They used unpolished, rough stone tools like hand axes, blades, and scrapers.
The first Palaeolithic tool (a hand axe) in India was discovered in Pallavarm ( in Southern India) by Robert Bruce Foote. Based on the environmental changes, this long period of the palaeolithic age can be divided into three phases.
- Lower Palaeolithic age.
- Middle Palaeolithic age.
- Upper Palaeolithic age.
Lower Palaeolithic age (up to 1,00,000 BCE)
- This age covers the greater part of the Ice age.
- The Stone tools used during this period were mainly made of a hard rock called Quartzite. Therefore, men of this age were known as Quartzite men in India.
- Tools mainly used were hand axes, cleavers, and choppers. These tools were mainly used for skinning, cutting, and digging the prey.
- This age was mostly represented by Sohan/Soan culture.
- Major sites of lower Palaeolithic age:
- Soan valley (in present Pakistan).
- Belan valley in Uttar Pradesh.
- Bhimbetka in Madhya Pradesh.
- Bidwana in Rajasthan.
- Bori in Maharashtra.
- Hunsgi in Karnataka.
- Other lower Palaeolithic sites were found in:
- Kashmir.
- Sites in the Thar Desert.
- Saurashtra, Gujarat.
- Central India.
- Narmada valley.
- North of the Kaveri river.
- The fossils of Homo erectus were found from Hathnora in Narmada valley in Madya Pradesh.
Middle Palaeolithic age (1,00,000 BCE to 40,000 BCE)
- It was the age of flakes. The tools mainly used were flakes, blades, scrapers, and pointers. These tools were lighter, smaller in size, and sharp in appearance.
- No houses were constructed. People mainly lived in caves and rock shelters.
- Neanderthal men dominated this period.
- Important sites of the middle Palaeolithic age:
- Bhimbetka in MP.
- Narmada river valley.
- Luni valley (Rajasthan).
- Tungabhadra river valley.
- Purulia in West Bengal.
- Nevasa in Maharashtra.
- Sanghao cave (in present Pakistan).
- Potwar Plateau (between Indus and Jhelum).
Upper Palaeolithic age (40,000 BCE to 10,000 BCE)
- This age saw the emergence of Homo sapiens.
- The age is mostly represented by Osteodontokeratic culture, in which tools were made up of bones, teeth, and horns. These tools were innovated.
- Rock paintings and carvings found in Bhimbedka were from this period which throughs light on the art & rituals of the Palaeolithic people. The animals depicted in these paintings were elephants, Bison, tigers, Rhino, and Boars.
- Important sites of the upper Palaeolithic age were:
- Belan in UP.
- Bhimbetka in MP.
- Chota Nagpur plateau.
- Maharashtra.
- Kurnool Caves.
- The Eastern Ghats in Andhra Pradesh.
- Bone tools have been found in cave sites of Kurnool and Muchchatla Chintamani Gavi (in Andhra Pradesh).
- Traces of ashes have been found in the Kurnool caves in Andhra Pradesh. This suggests that people were familiar with fire during the Upper Palaeolithic age.
Mesolithic Age (Middle Stone age: 10,000 BCE to 6000 BCE)
The term ‘Mesolithic’ also comes from two Greek words, ‘Meso‘ meaning Middle and ‘Lithic‘ meaning stone. This period belongs to the Holocene era when the temperature starts rising on the earth. The warm climate results in the melting of ice and also brought environmental changes. Stone tools of this period were generally tiny and sharper, also called microliths.
Important Characteristics of Mesolithic age
- It was a transitional phase between the Palaeolithic and Neolithic ages, sometimes also referred to as the Late Stone age.
- Initially, the people during this period lived on hunting, fishing, and food gathering, but later the domestication of animals was also seen for the first time. People start domesticating animals and cultivating plants. Dogs, Sheep, and goats were the earliest and the most domesticated animals.
- Due to favourable climate changes, a warm atmosphere, and better rainfall, there was a reduction in nomadism. Peoples start living in semi-permanent settlements. They start moving to new areas like nearby rivers, which provide them food security and water.
- The first human colonization of the Ganga Plains took place during this phase.
- Microliths (small and sharper stone tools) were the characteristic tools of this age. These small stone tools were probably stuck onto the handles of wood or bones to make tools like saws and sickles.
The tools used by the people include blades, spearheads, arrowheads, daggers, crescents, triangles, sickles, etc. These tools also help them to hunt small animals and birds during this period. - Mesolithic people initiated rock paintings. Many of the caves, and rock shelters in which these people lived had drawings or paintings on the walls. These paintings depict wild animals, hunting scenes, food collections, and dancing scenes.
- Burial practice became organized, which shows their belief in life after death.
Important sites of the Mesolithic period
- The earliest evidence of the domestication of animals came from Adamgarh in Madhya Pradesh.
Bagor in Rajasthan is the biggest Mesolithic site in India, where microliths, animal bones & shells have been excavated. - The earliest evidence of the burial of the dead was found from Langhnaj in Gujarat and Moharana Pahara in Uttar Pradesh.
- Other important Mesolithic sites:
- Bhimbetka caves, Kharwar, Joara, and Kathotia in Madhya Pradesh.
- Sarai Nahar Rai in Uttar Pradesh.
- Sundargarh, Sambalpur in Odisha.
- Biharanpur in West Bengal.
- Ezhuthu, Guha in Kerala.
Neolithic Period (New Stone Age: 6000 BCE to 1000 BCE)
The term ‘Neo‘ is a Greek word, which means ‘New’. The new stone age brings a Neolithic revolution, as it introduced a lot of changes in people’s social and economic life. Their lifestyle changed from nomadic to a settled one. This period saws the transformation of man from food gatherer to food producer. During this period, there was a development of settled agriculture.
Important Characteristics of the Neolithic period
- There was a settled pattern of life during this era. Neolithic people inhabited mainly near the rivers, and rock shelters in the hilly river valleys. People started to live in houses made of mud and reeds. They knew how to spin cotton, wool, and weave cloth and how make boats.
- People used tools and weapons made of polished stones and bones, such as borers, arrowheads, needles, scrapers, etc. They also used microlithic blades, chisels, celts, and polished hand axes. These tools make it easier for them to cultivate, hunt and perform other activities.
- Systematic agriculture started during this period. People cultivate lands and grew crops and fruits. They also domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats. The most cultivated crops during this period were Ragi, Horse gram, and Wheat.
- Pottery making emerged on a large scale during this period. People used these potteries to store their food, for cooking, etc. The pottery includes Grey ware, Black-burnished ware, and mat impressed ware. Initially, potteries were handmade, but later on, people used foot wheels to make pots.
Important sites of the Neolithic age
- The evidence of types of serial cultivation came from Koldihwa in Uttar Pradesh.
- Mehrgarh (Balochistan, Pakistan) was the earliest Neolithic site where people lived in houses made of sun-dried bricks.
- Burzahom, where people lived in pit dwellings to protect themselves from cold.
- The settlement pattern of life was first time observed in Inamgoan (Maharashtra).
- Other Important Neolithic sites:
- Gufkral in Kashmir (famous site for graveyards in houses).
- Chirand in Bihar.
- Piklihal, Utnur in Andra Pradesh.
- Hallur, Maski, Brahmagiri, Takkalkota in Karnataka.
- Paiyampalli in Tamil Nadu.
- In South India, Ash mounds have also been found.
