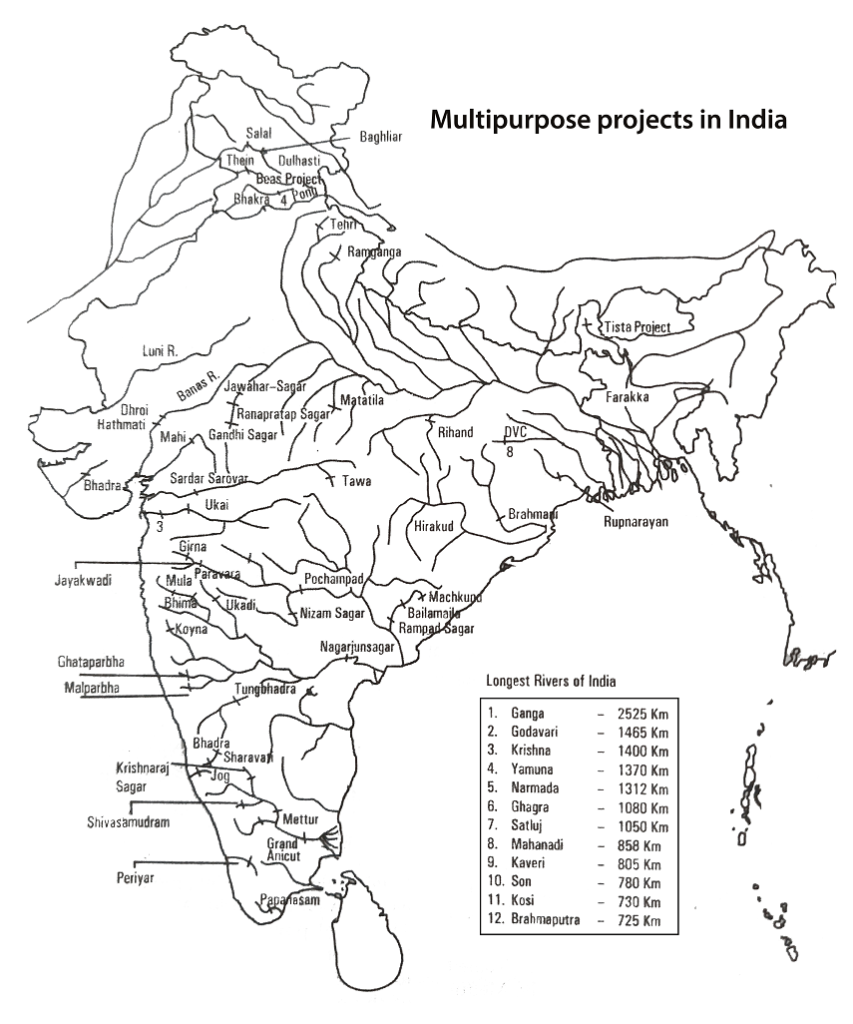
Multipurpose projects are designed for different works, such as irrigation, hydropower, flood control, tourism, etc., through the construction of dams. India is one of the leading producers of hydroelectricity as well as an agricultural country in the world.
In 1898, the first Hydroelectric project in India was commissioned at Darjeeling (West Bengal). The second hydroelectric plant was built at Mettur (Tamil Naidu) in 1899, followed by Sivasamudram (Kerala) in 1902. In 1909, the fourth hydropower project was commissioned on the Jehlum river.
After the Independence, especially in the First Five-year plan, great emphasis was given to agriculture and electricity development. Several Multipurpose projects were constructed, such as Hirakud Dam and Bhakra-Nangal Dam. In this article, we’re going to discuss important multipurpose projects in India.
Bhakra Nangal Project
The Bhakra-Nangal Dam is one of the highest straightway gravity dams in the world. It is constructed across the Satluj river near Bhakra George (in Himachal Pradesh), with a joint venture of the Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan governments, and funded by Central Government. The dam is built to produce electricity, flood control, silt control, provides irrigation, soil conservation, and preserve wildlife. The project mainly consists of two dams.
- Bhakra Dam: The dam is 518m long, having a height of 226 meters. Its reservoir is popularly known as Gobind Sagar.
- Nangal Dam: It has been constructed 13km downstream of the Bhakra dam to maintain the stability of the channel. It is 305m long, 30m high, and 121m wide. It is situated at Nangal village of Ropar district.
The project also comprises the Kotla and Ganguwal hydel projects based on the 64km long Nagal channel between Nagal and Ropar to generate hydel power.
Damodar Valley Project
Damodar river often called the “Sorrow of Bengal“, is the tributary of the Hugli River. It follows through Jharkhand and West Bengal. The Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC) was established in 1948, making it the first multipurpose river valley project of India after Independence. It was built on the patterns of the USA’s Tennessee river valley authority.
The Damodar Valley project consists of seven dams across the Damodar river and its tributaries. Out of these seven dams, four storage dams are constructed at Tilaiya, Konar, Maithan, Panchet, and three thermal power stations are installed at Aiyar, Bokaro, and Balpahri.
- Tilaiya Dam: This concrete dam was constructed across the Barakar river in the Koderma district of Jharkhand. Tilaiya dam was completed in 1953. It provides irrigation to forty thousand hectares of land and helps in flood reduction.
- Konar Dam: It has been built across the Konar River (a tributary of the Damodar river), which lies in the Hazaribagh district of Jharkhand. This dam was completed in 1955. Konar dam also provides cooling water to the Steel Plant at Bokaro.
- Maithon Dam: This 56m high dam has been constructed across the Barakar river near the confluence of Barakar with Damodar river, in Jharkhand. This dam was completed in 1958.
- Panchet Dam: The Panchet hill dam has been constructed across the Damodar river, in the Dhanbad district of Jharkhand. It is 2545m long with a height of 45m. The dam was completed in 1959.
- Aiyar, Bokaro, and Balpahri dams have been constructed on the Damodar and Barakar rivers.
Hirakud Project
Hirakud Dam is considered to be the longest dam in the world. It is a 14 km-long dam constructed across the Mahanadi river. Its construction began in 1947, but the dam was started in 1957.
The entire project involves three dams across the Mahanadi river, at Hirakud, Tikrapara, and Naraj. Hirakud Dam lies near the Sambalpur district of Odisha. Tikrapara and Naraj dam lie near Cuttack district.
Beas Project
Beas Project is one of the biggest multipurpose projects in India. It is a joint venture of the state of Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan. The project has two units. One is Beas-Sutlej Link, and the other is Beas Dam at Pong. Its construction began in 1961.
Beas Dam is earthquake-proof with an estimated height of 133m. The main objective of the project is to meet the growing needs for irrigation and electricity demand.
Chambal Valley Project
Chambal Valley Project is an important multipurpose project in Western India. It is built across the Chambal river (a tributary of the Yamuna river), with a joint venture of the Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh governments. The project comprises three dams –Gandhi Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, and Jawahar Sagar dams.
- Gandhi Sagar dam: This dam is constructed in Madhya Pradesh across the Chambal river. It provides electricity and irrigation to the surrounding regions of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- Rana Pratap Sagar dam: It is constructed across the Chambal river in the Kota district of Rajasthan.
- Jawahar Sagar dam: This dam is constructed to the north of Rana Pratap Sagar dam in Rajasthan. The project generates electricity and provides irrigation water to the catchment area.
Kosi Project
This project is a joint undertaking of the Indian and Nepal governments. It is built across the Kosi river, the most unpredictable river in Bihar, also known as the “Sorrow of Bihar“. A 3-mile long barrage has been constructed near Hanumannagar in Nepal. The project’s main objective is to control floods, build canals for irrigation, and generate electricity.
Nagarjuna Sagar Project
Nagarjuna Sagar Project has been constructed across the Krishna river near the border between Nalgonda district in Telangana and Guntur district in Andra Pradesh. The right and left bank canals have been named after Jawaharlal Nehru and Lal Bahadur Shastri, respectively. It is also the largest masonry dam in India (even in the world). It supplies electricity to Hyderabad, Guntur, Khammam, Nalgonda, and Vijayawada.
Rihand Project
Rihand Project is the largest multipurpose river valley project in Uttar Pradesh. It has been constructed across the Rihand river (a tributary of the Son river) in the Sonbhadra district (near Mirzapur) of Uttar Pradesh. Its large reservoir is popularly known as Gobind Ballav Pant Sagar.
Rihand Project gets funded by the Central government. It supplies electricity to eastern Uttar Pradesh, western Bihar, and northern Madhya Pradesh. It also helps to control floods and soil erosion in Son valley.
Tehri Dam
Tehri Dam is Asia’s largest and World’s Fifth largest hydroelectric project. It is also the tallest dam in India, with a height of 260 meters. It is a rock and earth-fill embankment dam that has been constructed across the Bhagirathi river in the Tehri district of Uttarakhand. The estimated power generated by the dam is 1000MW.
Tungabhadra Project
Tungabhadra Dam, also known as Pampa Sagar, has been constructed across the Tungabhadra river (a right-hand tributary of the Krishna river), at Mallapuram, near Hospet in the Bellary district of Karnataka. The project is a joint undertaking of Karnataka and Andra Pradesh. Tungabhadra canals provide irrigation to more than 4 lakh hectares of arable land.
Sardar Sarovar Dam
This project has been constructed across the Narmada river, in Navagoan near Kevadiya, in the Narmada district of Gujarat. Its concrete dam with a height of 163m. It supplies electricity to Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra. It will also promote livestock keeping, dairy farming, and animal husbandry.
Farakka Barrage
Farakka Project is an important multipurpose project of West Bengal, build across the Ganga river in the Murshidabad district of West Bengal. The main objectives of the project are water transportation and irrigation. It aims to improve the navigation at the Hooghly river and maintain the Calcutta Port.

It’s good 👍.